The Middle Ages or Dark Ages
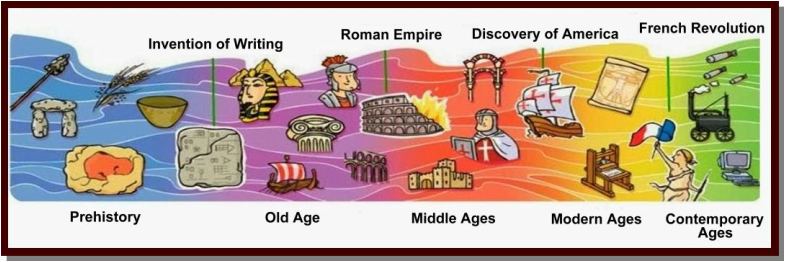
The Middle Ages, or Medieval Times, in Europe was a long period of history from the year 476 (the fall of the Roman Empire) to 1500 approximately.
This was a time of castles and peasants, guilds and monasteries, cathedrals and crusades. Great leaders such as Juana de Arco and Carlomagno were part of the Middle Ages as well as events such as the Black Plague and the rise of Islam.
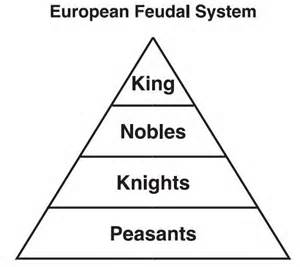
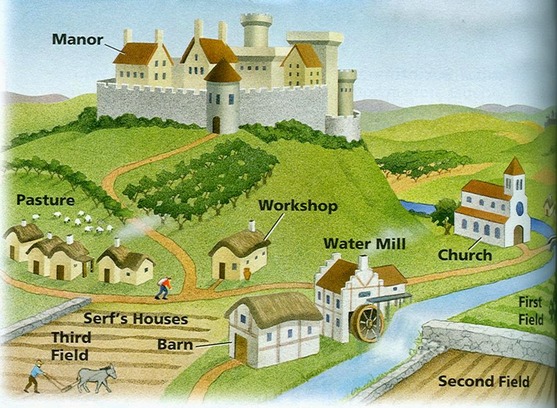
In the Middle Ages most people lived on a manor in the country. A manor was a village with a castle, a church and some land around it. The king gave land to his most important noblemen and bishops. In return, they promised to give the king soldiers for his armies.
The Peasants
The lowest people of society were the peasants. They didn't have their own land, but they got land from the lords . The lords also gave them protection.
The lowest people of society were the peasants. They didn't have their own land, but they got land from the lords . The lords also gave them protection.
Peasants worked on the land and produced the goods that the lord needed. But they did not have a very nice life. They had to pay a lot of taxes and give the lord much of their harvests.
Poor people didn't get very much to eat. They had to eat dark bread because white bread was only for the king and his family. Only rich people had meat to eat.
Peasants lived in rustic country huts; the family animals, such as a cow, may also live inside the home. The home was usually dark, smoky from the fire, and uncomfortable.
Poor people didn't get very much to eat. They had to eat dark bread because white bread was only for the king and his family. Only rich people had meat to eat.
Peasants lived in rustic country huts; the family animals, such as a cow, may also live inside the home. The home was usually dark, smoky from the fire, and uncomfortable.
The Knights
The knights were nobles who also fought in battles and tournaments. There were three types of soldiers during the Middle Ages: foot soldiers, archers, and knights. The knights were armored soldiers who rode on horses. Only the wealthiest nobles could afford to be a knight. They needed very expensive armor, weapons, and a powerful war horse.
The knights were nobles who also fought in battles and tournaments. There were three types of soldiers during the Middle Ages: foot soldiers, archers, and knights. The knights were armored soldiers who rode on horses. Only the wealthiest nobles could afford to be a knight. They needed very expensive armor, weapons, and a powerful war horse.
The Nobles
Lords, ladies and were called nobles. Knights were also nobles. They had a much higher status in medieval society than that of the peasants. The peasants served the nobles and were controlled by them.
A Lord had complete authority over his lands and the people who lived on his lands.
Lords, ladies and were called nobles. Knights were also nobles. They had a much higher status in medieval society than that of the peasants. The peasants served the nobles and were controlled by them.
A Lord had complete authority over his lands and the people who lived on his lands.
A Lady had very few rights. She was expected to marry whoever her father chose and could be married at an age as young as twelve years old. Her responsibilities were to care for the household, and raise children.
A Knight served his lord during times of battle, which was frequent. He enjoyed more freedoms and rights than peasants, but his life was always dangerous.
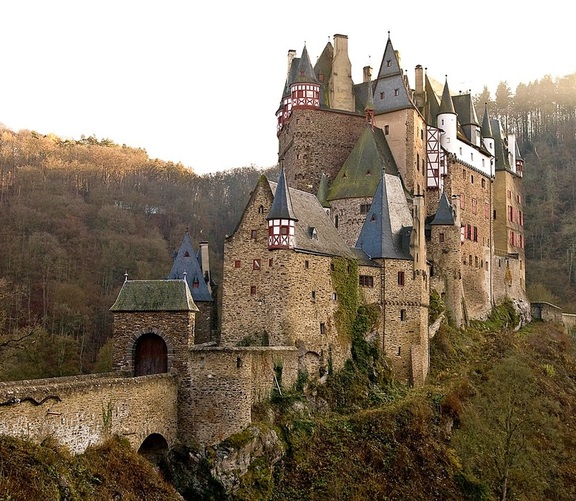
The castles were beautiful from the outside, but they were damp, smelly, and cold on the inside. They were built to protect the lords and ladies, not to be comfortable.
The Power of the Church
Catholic Church got so much power in the Middle Ages. The Pope had even more power than the very same Kings. Local bishops also got a lot of power, influence and, above all, wealth. Because the leaders of the Church were almost always nobles, they received lands and wealth from the king, and also peasants who served them. Other nobles often paid them tributes in hopes of obtaining the grace of God...
Catholic Church got so much power in the Middle Ages. The Pope had even more power than the very same Kings. Local bishops also got a lot of power, influence and, above all, wealth. Because the leaders of the Church were almost always nobles, they received lands and wealth from the king, and also peasants who served them. Other nobles often paid them tributes in hopes of obtaining the grace of God...
As the Middles Ages went on, Priests, Bishops and Church in general obtained such a high power in society that they even decided on political decisions of their kingdoms.
Life in the Cities
City life was very different from country life, but it wasn't much easier. The cities were crowded and dirty. A lot of people worked as craftsmen and were members of a guild. Young boys would serve as apprentices for seven years learning a craft. Other jobs in the city included servants, merchants, bakers, doctors, and lawyers.
City life was very different from country life, but it wasn't much easier. The cities were crowded and dirty. A lot of people worked as craftsmen and were members of a guild. Young boys would serve as apprentices for seven years learning a craft. Other jobs in the city included servants, merchants, bakers, doctors, and lawyers.
City homes were very crowded and usually everyone slept in the same room. They were usually dirty, unhealthy and provided a narrow (very small) space for their occupants.
Did children go to School?
Very few people attended school in the Middle Ages. Schools didn't exist as we know them today.
Most peasants' children learned their job and how to survive from their parents.
Some children learned a craft through their parents' lessons.
Only rich, princes or noble children often learned through personal teachers in individual or small-group classes. They would go to live in the castle of another lord where they would work for the lord, learning about how a large manor was run.
There were some schools run by the church. Here students would learn to read and write Latin. The first universities also began during the Middle Ages.
Very few people attended school in the Middle Ages. Schools didn't exist as we know them today.
Most peasants' children learned their job and how to survive from their parents.
Some children learned a craft through their parents' lessons.
Only rich, princes or noble children often learned through personal teachers in individual or small-group classes. They would go to live in the castle of another lord where they would work for the lord, learning about how a large manor was run.
There were some schools run by the church. Here students would learn to read and write Latin. The first universities also began during the Middle Ages.
Watch The Middle Ages in 3 1/2 Minutes:
Between Ancient and Modern
In 476CE, warriors attacked the city of Rome and ended more than 800 years of glory for the "Eternal City." Historians mark the fall of Rome as the end of ancient history. The next one thousand years were called the Middle Ages. The Latin term for Middle Ages is "medieval."
The beginning of the Middle Ages is often called the "Dark Ages" because the great civilizations of Greece and Rome had fallen. Life in Western Europe during the Middle Ages was very hard. Very few people could read or write and nobody expected conditions to improve. The only hope for most people during the Middle Ages was their strong belief in Christianity, and the hope that life in heaven would be better than life on Earth.
The Dark Ages were anything but dark in other parts of the world. The Muslims in the Middle East and North Africa studied and improved on the works of the ancient Greeks while civilization flourished in sub-Saharan Africa, China, India, and the Americas.
Europe began to experience great change by about 1450. Within one hundred years, Columbus had sailed to America, literacy spread, scientists made great discoveries, and artists created work that still inspires us today. Historians call the next period of European history the "Renaissance," or the "rebirth." The Renaissance is the beginning of modern history.
In 476CE, warriors attacked the city of Rome and ended more than 800 years of glory for the "Eternal City." Historians mark the fall of Rome as the end of ancient history. The next one thousand years were called the Middle Ages. The Latin term for Middle Ages is "medieval."
The beginning of the Middle Ages is often called the "Dark Ages" because the great civilizations of Greece and Rome had fallen. Life in Western Europe during the Middle Ages was very hard. Very few people could read or write and nobody expected conditions to improve. The only hope for most people during the Middle Ages was their strong belief in Christianity, and the hope that life in heaven would be better than life on Earth.
The Dark Ages were anything but dark in other parts of the world. The Muslims in the Middle East and North Africa studied and improved on the works of the ancient Greeks while civilization flourished in sub-Saharan Africa, China, India, and the Americas.
Europe began to experience great change by about 1450. Within one hundred years, Columbus had sailed to America, literacy spread, scientists made great discoveries, and artists created work that still inspires us today. Historians call the next period of European history the "Renaissance," or the "rebirth." The Renaissance is the beginning of modern history.